728x90
728x90
애저(Azure) Machine Learning Service의 Notebooks 사용해보기
들어가며
- Azure Machine Learning Service의 Notebooks를 이용하여 실습해보자.
- Azure Machine Learning Service 배포 방법은 이전 글(https://dev-astra.tistory.com/400)을 참고한다.
실습하기
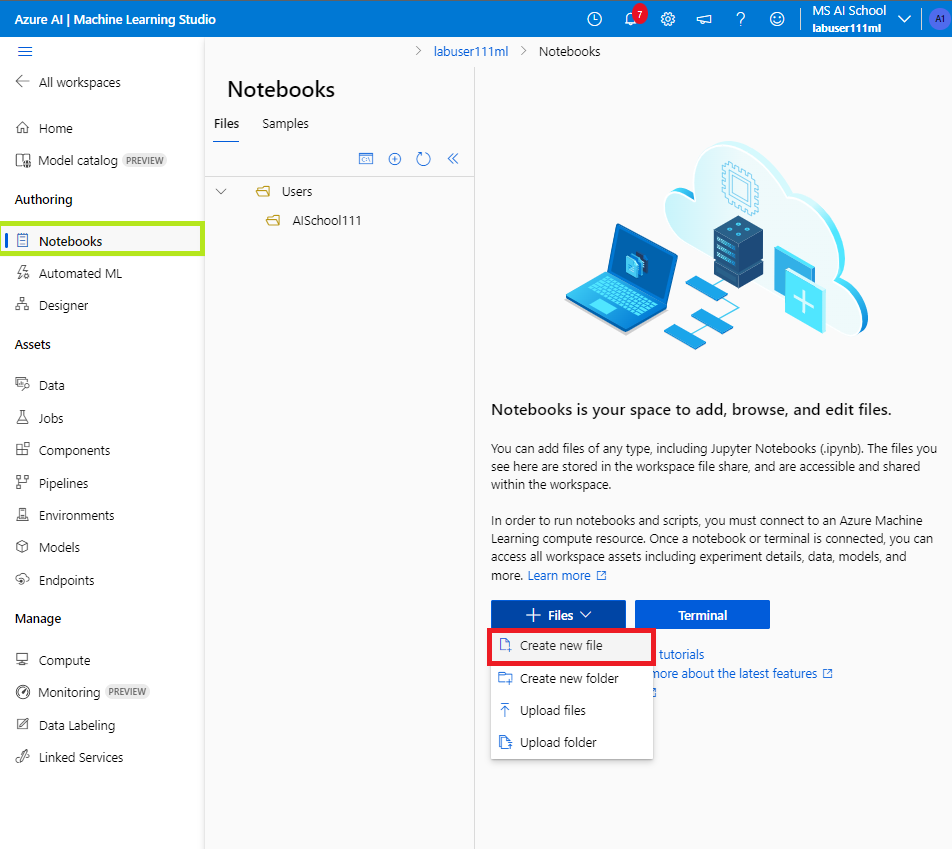
- @[Authoring]@ 섹션에서 @[Notebooks]@ 탭을 클릭한다. 그리고 @[Files]@ 버튼을 클릭하고, @[Create new file]@을 선택한다. 그리고 @.ipynb@ 파일을 하나 만들어준다.
 |
 |
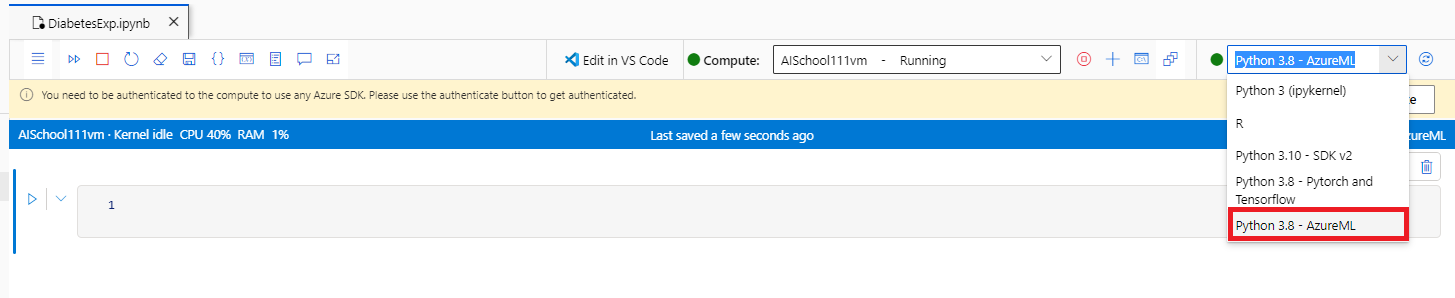
- 그리고 실행 환경을 @[Python 3.8 - AzureML]@로 바꿔준다.
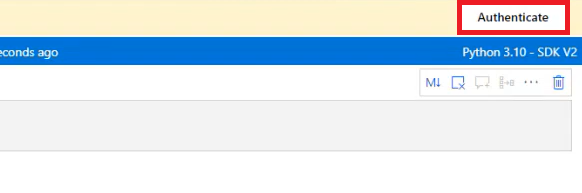
- 다음 처럼 인증을 해준다. 우측 상단의 @[Authenticate]@ 버튼을 클릭하면 다시 로그인을 하게 된다.
 |
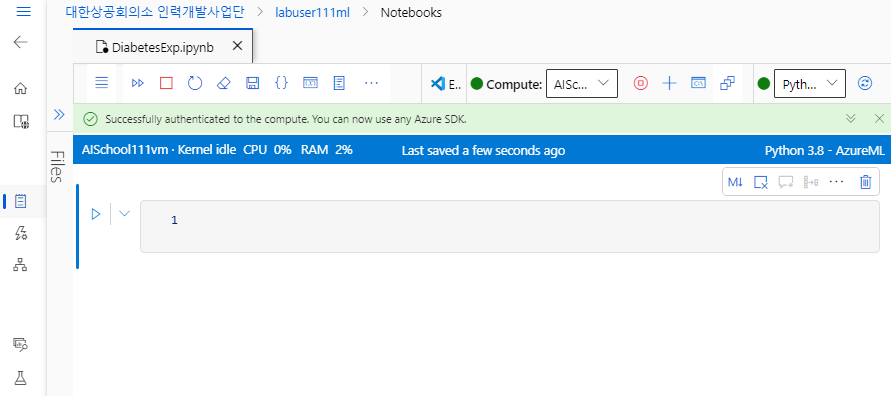 |
실습 전, 다음 2가지를 확인한다.
① 인증 완료, ② 실행 환경을 Python 3.8 AzureML로 설정하기
- 워크 스테이션의 상태를 확인해본다.
from azureml.core import Workspace
ws = Workspace.from_config() # 워크 스테이션의 상태 확인
print('Workspace name: ' + ws.name, '\n',
'Azure Region: ' + ws.location, '\n',
'Subscription ID: ' + ws.subscription_id, '\n',
'Resource Group: ' + ws.resource_group
)
- 실험 공간을 준비한다.
from azureml.core import Experiment
experiment = Experiment(workspace=ws, name='diabetes-experiment') # 워크 스페이스와 시험의 이름 지정
- 데이터를 준비해본다.
from azureml.opendatasets import Diabetes
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_df = Diabetes.get_tabular_dataset().to_pandas_dataframe().dropna()
y_df = x_df.pop('Y') # Y를 끄집어 낸다.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x_df, y_df, test_size=0.2, random_state=66)
print(X_train)
- 모델 훈련, 로그, 모델 파일 관리를 해본다. 이 코드를 실행하면 Azure Machine Learning Service에 모델 파일이 업로드 된다.
# 모델 훈련, 로그, 모델 파일 관리
from sklearn.linear_model import Ridge
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import math
alphas = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1]
for alpha in alphas:
# 실험의 로그 기록
run = experiment.start_logging()
run.log('alpha_value', alpha) # alpha_value에 alpha 값을 대입한다.
model = Ridge(alpha=alpha)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
rmse = math.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
run.log('rmse', rmse) # rmse에 rmse 값을 대입한다.
print('model_alpha={0}, rmse={1}'.format(alpha, rmse))
# 모델을 파일로 저장하기
model_name = 'model_alpha_' + str(alpha) + '.pkl' # 모델 이름 지정하기
filename = 'outputs/' + model_name
joblib.dump(value=model, filename=filename)
# Azure ML Service에 모델 파일을 업로드 하기
run.upload_file(name=model_name, path_or_stream=filename)
run.complete() # 로그 기록을 끝낸다.
print(f'{alpha} experiment completed.')

- 실험이 끝나면, @outputs@ 디렉터리에서 저장한 사이킷런의 모델 파일들(@.pkl@)을 볼 수 있다.
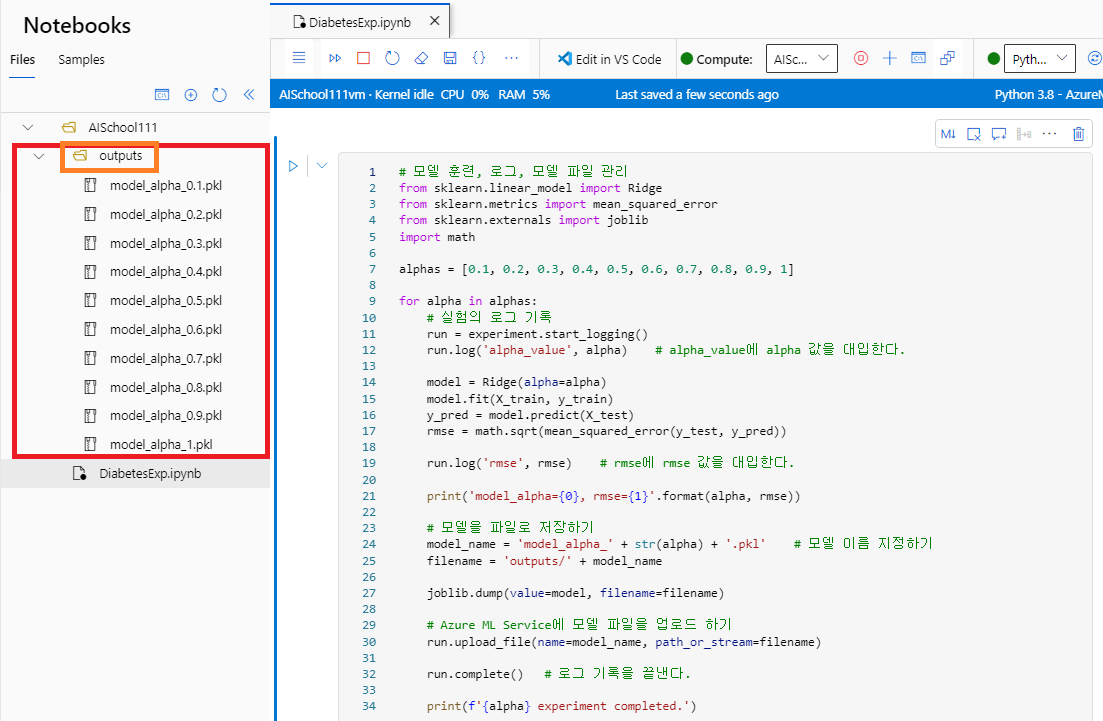
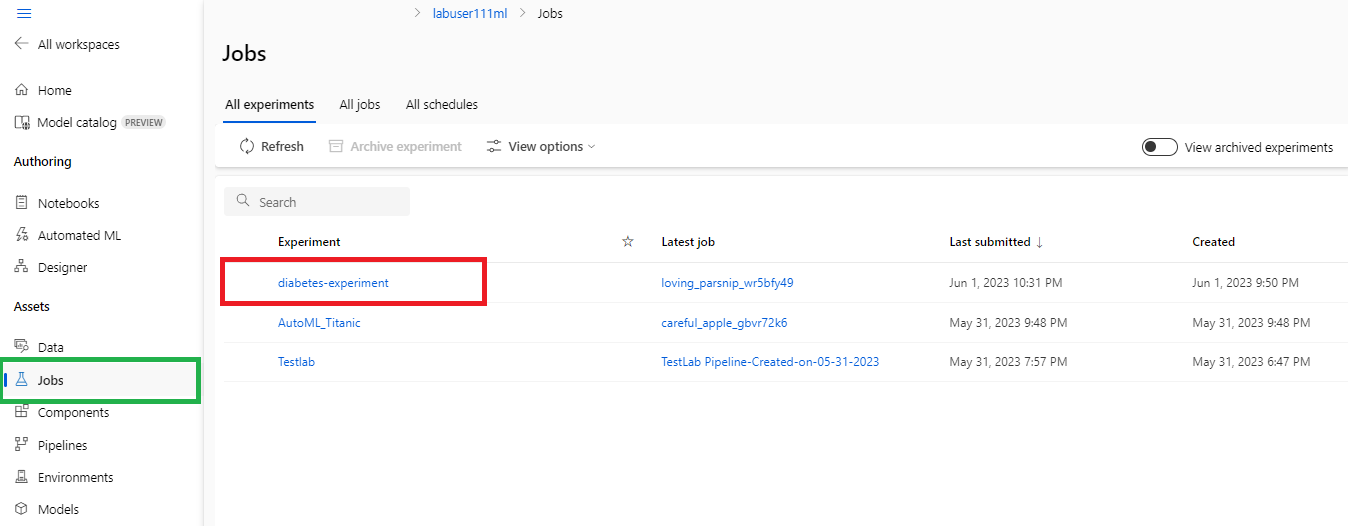
- 그리고 좌측의 @[Jobs]@ 탭에서 업로드한 모델 파일(@diabetes-experiment@)을 확인할 수 있다.
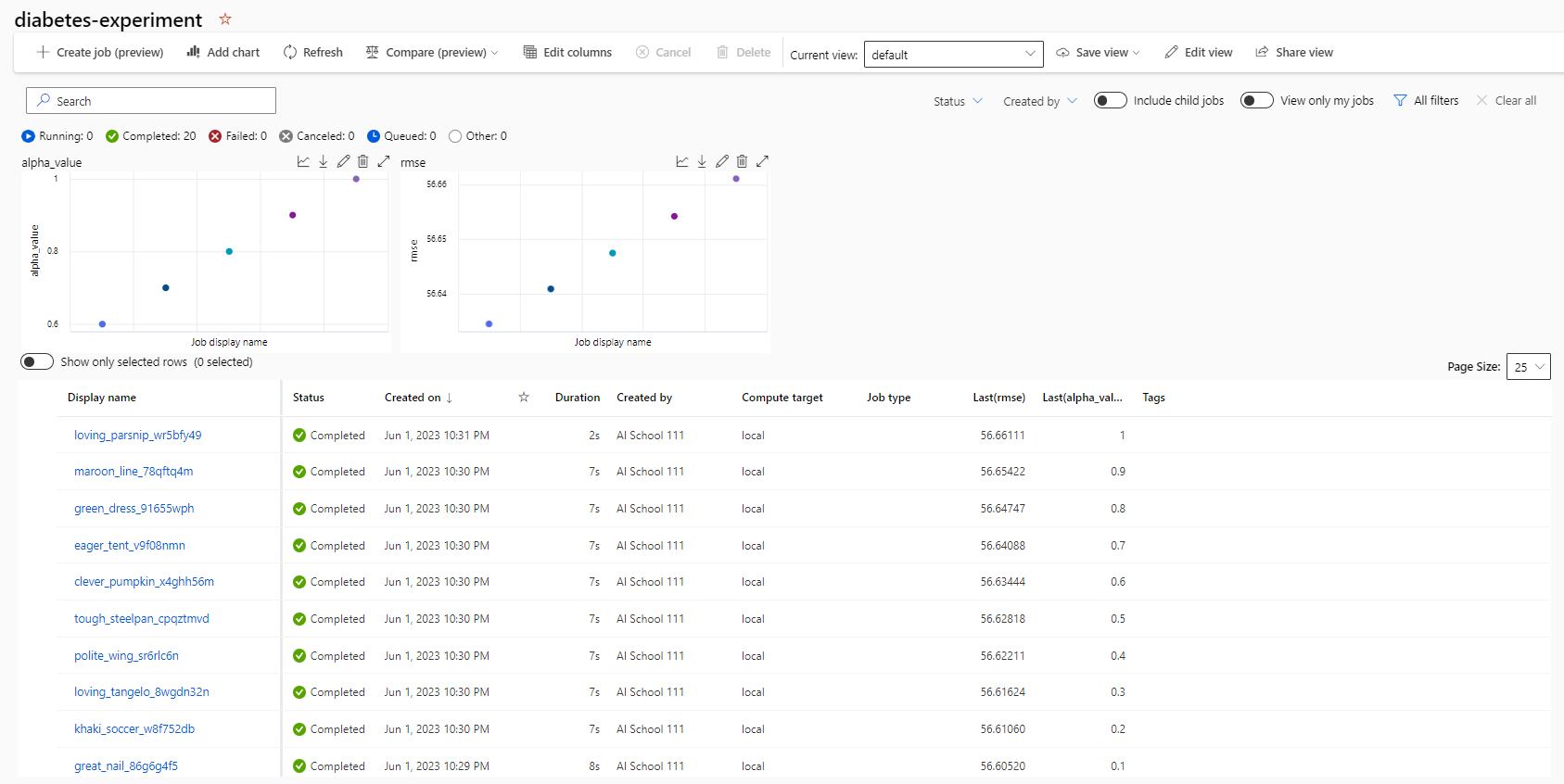
- 해당 링크를 클릭하면 모델의 여러 가지 정보들을 확인할 수 있다.
- Azure ML Service에 업로드한 작업 공간을 연동한다.
from azureml.core import Experiment
experiment = Experiment(workspace=ws, name="diabetes-experiment")
experiment
- 최고의 모델을 탐색하고 다운로드 해본다.
# Best Model 탐색 후 다운로드
minimum_rmse = None
minimum_rmse_runid = None
for exp in experiment.get_runs():
run_metrics = exp.get_metrics()
run_details = exp.get_details()
run_rmse = run_metrics['rmse']
run_id = run_details['runId']
# 가장 낮은 rmse 값을 가진 실행 ID를 구하기
if minimum_rmse is None: # 제일 처음 실행시켰을 경우
minimum_rmse = run_rmse
minimum_rmse_runid = run_id
else:
if run_rmse < minimum_rmse:
minimum_rmse = run_rmse
minimum_rmse_runid = run_id
print('Best run_id: ' + minimum_rmse_runid)
print('Best run_id rmse: ' + str(minimum_rmse))
- Best Model을 다운로드 받아본다.
from azureml.core import Run
best_run = Run(experiment=experiment, run_id=minimum_rmse_runid)
print(best_run.get_file_names())
best_run.download_file(name=str(best_run.get_file_names()[0]))
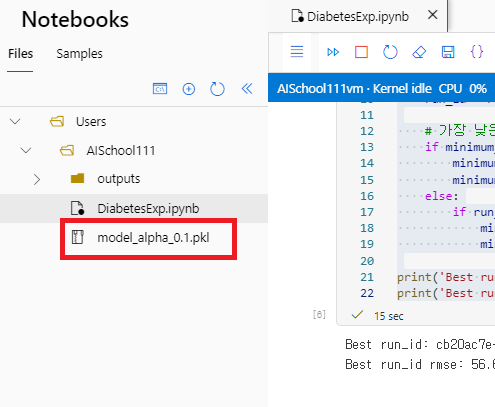
- Best Model의 정보가 담긴 모델 파일이 다운로드 받아진 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- 다음 코드를 작성하여, 모델에서 사용했던 Feature와 Label을 각각 @.csv@ 파일로 저장해본다.
import numpy as np
from azureml.core import Dataset
np.savetxt('feature.csv', X_train, delimiter=',') # Feature 데이터 저장
np.savetxt('label.csv', y_train, delimiter=',') # Label 데이터 저장
- 다음 코드를 작성하여 Data Store에 csv 파일들을 업로드 해본다.
# Data Store에 업로드 하기
datastore = ws.get_default_datastore() # Data Store 정보 가져오기
datastore.upload_files(files=['./feature.csv', './label.csv'],
target_path='diabetes-experiment/', # 업로드할 경로
overwrite=True # 덮어쓰기 가능
)
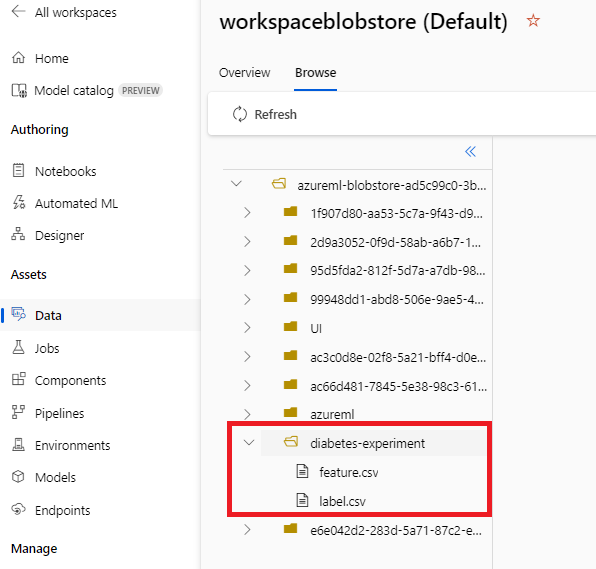
- 그리고 다음과 같이 @[Data]@ 탭 > @[Datastores]@ 탭 > @[workspaceblobstore (Default)]@에 진입한다.
 |
 |
- 다음 명령을 실행하여 Data Store에서 방금 업로드한 파일들을 가져와본다.
feature_dataset = Dataset.Tabular.from_delimited_files(path=[(datastore, 'diabetes-experiment/feature.csv')]) # 해당 경로에 있는 파일들을 가져온다.
label_dataset = Dataset.Tabular.from_delimited_files(path=[(datastore, 'diabetes-experiment/label.csv')])
- 다음 명령을 실행하여 생성했었던 Best Model을 Data Store에 등록해본다. @[Models]@ 탭에서 업로드한 Best Model을 확인할 수 있다.
import sklearn
from azureml.core import Model
from azureml.core.resource_configuration import ResourceConfiguration
# 모델의 등록
model = Model.register(workspace=ws,
model_name='diabetes-experiment-data',
model_path=f'./{str(best_run.get_file_names()[0])}',
model_framework=Model.Framework.SCIKITLEARN, # 사이킷런
model_framework_version=sklearn.__version__,
sample_input_dataset=feature_dataset,
sample_output_dataset=label_dataset,
resource_configuration=ResourceConfiguration(cpu=1, memory_in_gb=0.5), # 실행 환경 지정 : CPU 1개, 0.5GB RAM
description='Ridge Regression Model to predict diabetes progression',
tags={'area' : 'diabetes', 'type' : 'regression'}
) |
 |
- 다음 명령을 실행하여 모델 정보를 확인해본다.
print('Model Name: ', model.name)
print('Model Version: ', model.version)
- 다음 명령을 실행하여 생성한 모델을 배포(Deployment) 해본다. 마치기 까지 시간이 꽤 걸린다.
service_name = 'diabetes-service'
service = Model.deploy(ws, service_name, [model], overwrite=True) # 모델은 여러 개 배포할 수 있기 때문에 리스트 타입으로 표현한다.
service.wait_for_deployment(show_output=True)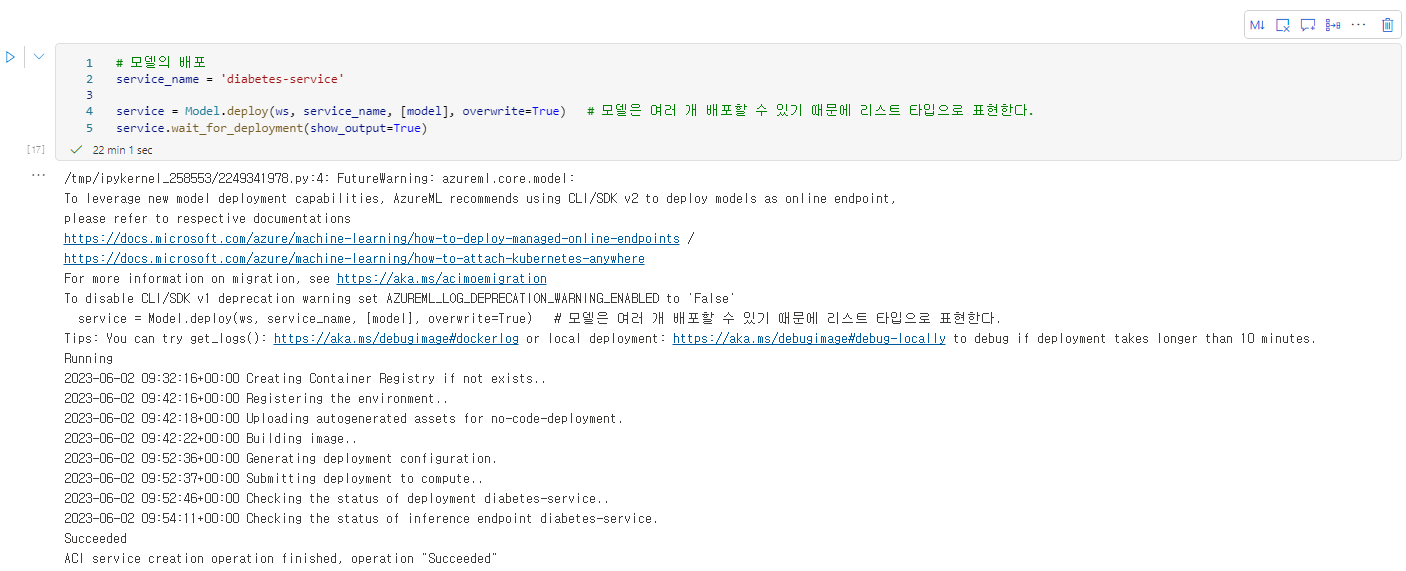
- 배포가 완료되면, 엔드포인트(Endpoint)를 확인해본다.
 |
 |
- @REST endpoint@를 복사해서 사용하면, 이 모델을 사용하여 다른 데이터의 분석 및 예측 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
- 다음과 같이 @[Test]@ 탭에서 간단하게 테스트도 해볼 수 있다.

- 다음 명령을 실행하여 서비스 안에서 배포된 모델을 이용하여 예측 작업을 수행해본다.
import json
input_payload = json.dumps({
'data': X_train[0:2].values.tolist(),
'method': 'predict'
})
output = service.run(input_payload)
print(output)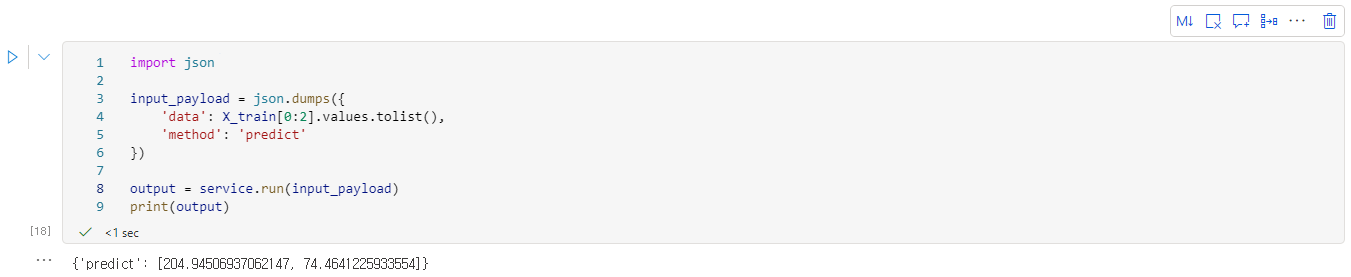
- 이밖에도, 엔드포인트(Endpoint)를 이용하면 편하게 모델을 끌여와 사용할 수 있다.
- 지금까지 간단하게 데이터를 가공하여 모델을 만든 후, 예측 작업을 해보고, 모델을 Azure에 업로드하여 서비스로 배포해보는 과정을 진행해 보았다.

이와 같은 작업을 통해 AI 모델을 배포하고 웹, 앱 등에서 필요할 때 끌어와 쓸 수 있다.
참고 사이트
Azure Machine Learning 설명서
Azure Machine Learning을 통해 모델을 학습 및 배포하고 ML 수명 주기를 관리(MLOps)하는 방법을 알아봅니다. 자습서, 코드 예제, API 참조 등
learn.microsoft.com
자습서: 모델 학습 - Azure Machine Learning
모델 학습 프로세스 살펴보기
learn.microsoft.com
자습서: Notebook을 사용하여 예측 모델 만들기(2-1부) - Azure Machine Learning
Jupyter Notebook의 코드를 사용하여 기계 학습 모델을 빌드하고 배포하는 방법을 알아봅니다. 또한 Microsoft Power BI에 쉽게 통합할 수 있도록 입력 및 출력을 정의하는 채점 스크립트를 만듭니다.
learn.microsoft.com
728x90
728x90
'DevOps > Azure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Azure] Azure App Services 프로젝트 배포 후, Cannot find module 오류 해결법 (0) | 2025.07.12 |
|---|---|
| [Azure] Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB (RU) 연동하기 (1) | 2025.07.11 |
| [Azure] App Services에 Next.js 15 배포하기 (VS Code, LocalGit) (3) | 2025.06.05 |
| [Azure] Visual Studio 서비스를 이용하여 CRUD 애플리케이션 제작하기 (0) | 2023.06.07 |
| [Azure] Azure Machine Learning Service 사용해보기 : Automated ML (0) | 2023.05.31 |
| [Azure] Azure Machine Learning Service 사용해보기 : Designer (0) | 2023.05.31 |
| [Azure] 쿠버네티스(Kubernetes) 실습하기 : AKS(Azure Kubernetes Service) 실습 (0) | 2023.05.30 |
| [Azure] 쿠버네티스(Kubernetes) 실습하기 : 간단한 실습 해보기 (0) | 2023.05.29 |
